
EC-COUNCIL CEH v12 dumps are the latest and most effective exam solution to aid candidates in their pre-exam practice!
EC-COUNCIL CEH v12 dumps have been updated! Reviewed, corrected, and actually verified by the EC-Council team, it is true and effective! Meet the conditions for successfully passing the EC-COUNCIL CEH v12 certification exam.
EC-COUNCIL CEH v12 dumps contain 528 latest exam questions and answers, which truly cover all EC-COUNCIL CEH V12 exam requirements.
Use the latest and most effective EC-COUNCIL CEH v12 certification exam solution: Download EC-COUNCIL CEH v12 dumps with PDF and VCE: https://www.leads4pass.com/312-50v12.html to help you study easily and successfully pass the EC-COUNCIL certification exam.
And share some EC-COUNCIL CEH v12 dumps exam questions online practice for free:
| From | Number of exam questions | Associated certification |
| leads4pass | 15 | ECSA,CEH v11,CEH v10,EC-COUNCIL |
Question 1:
Samuel a security administrator, is assessing the configuration of a web server. He noticed that the server permits SSlv2 connections, and the same private key certificate is used on a different server that allows SSLv2 connections. This vulnerability makes the web server vulnerable to attacks as the SSLv2 server can leak key information.
Which of the following attacks can be performed by exploiting the above vulnerability?
A. DROWN attack
B. Padding oracle attack
C. Side-channel attack
D. DUHK attack
Correct Answer: A
DROWN is a serious vulnerability that affects HTTPS and other services that deem SSL and TLS, some of the essential cryptographic protocols for net security. These protocols allow everyone on the net to browse the net, use email, look online, and send instant messages while no third parties are able to browse the communication.
DROWN allows attackers to break the encryption and read or steal sensitive communications, as well as passwords, credit card numbers, trade secrets, or financial data.
At the time of public disclosure on March 2016, our measurements indicated thirty third of all HTTPS servers were vulnerable to the attack. fortuitously, the vulnerability is much less prevalent currently. As of 2019, SSL Labs estimates that one.2% of HTTPS servers are vulnerable.
What will the attackers gain? Any communication between users and the server. This typically includes, however, isn’t limited to, usernames and passwords, credit card numbers, emails, instant messages, and sensitive documents. under some common scenarios, an attacker can also impersonate a secure website and intercept or change the content the user sees.
Who is vulnerable? Websites, mail servers, and other TLS-dependent services are in danger from the DROWN attack.
At the time of public disclosure, many popular sites were affected. we used Internet-wide scanning to live how many sites are vulnerable:

SSLv2 Operators of vulnerable servers got to take action. there\’s nothing practical that browsers or end-users will do on their own to protect against this attack. Is my site vulnerable?
Modern servers and shoppers use the TLS encryption protocol. However, because of misconfigurations, several servers also still support SSLv2, a 1990s-era precursor to TLS.
This support did not matter in practice, since no up-to-date clients really use SSLv2. Therefore, despite the fact that SSLv2 is thought to be badly insecure, until now, simply supporting SSLv2 wasn’t thought of as a security problem, clients never used it.
DROWN shows that merely supporting SSLv2 may be a threat to fashionable servers and clients. It modern associate degree attacker to modern fashionable TLS connections between up-to-date clients and servers by sending probes to a server that supports SSLv2 and uses the same private key.
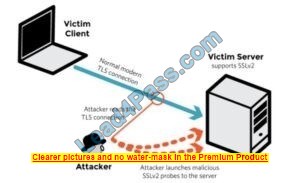
SSLv2
It allows SSLv2 connections. This is surprisingly common, due to misconfiguration and inappropriate default settings.
Its private key is used on any other server that allows SSLv2 connections, even for another protocol. Many companies reuse the same certificate and key on their web and email servers, for instance. In this case, if the email server supports SSLv2 and the web server does not, an attacker can take advantage of the email server to break TLS connections to the web server.
A server is vulnerable to DROWN if:

SSLv2 How do I protect my server? To protect against DROWN, server operators need to ensure that their private keys software is used anyplace with server computer code that enables SSLv2 connections.
This includes net servers, SMTP servers, IMAP and POP servers, and other software that supports SSL/TLS.
Disabling SSLv2 is difficult and depends on the particular server software. we offer instructions here for many common products: OpenSSL: OpenSSL may be a science library employed in several server merchandises.
For users of OpenSSL, the simplest and recommended solution is to upgrade to a recent OpenSSL version. OpenSSL 1.0.2 users ought to upgrade to 1.0.2g. OpenSSL 1.0.1 users ought to upgrade to one.0.1s. Users of older OpenSSL versions ought to upgrade to either one in every one of these versions. (Updated March thirteenth, 16:00 UTC) Microsoft IIS (Windows Server): Support for SSLv2 on the server aspect is enabled by default only on the OS versions that correspond to IIS 7.0 and IIS seven.5, particularly Windows Scene, Windows Server 2008, Windows seven, and Windows Server 2008R2.
This support is disabled within the appropriate SSLv2 subkey for `Server\’, as outlined in KB245030. albeit users haven’t taken the steps to disable SSLv2, the export-grade and 56-bit ciphers that build DROWN possibly don’t seem to be supported by default.
Network Security Services (NSS): NSS may be a common science library designed for several server merchandises.
NSS version three.13 (released back in 2012) and higher than ought to have SSLv2 disabled by default. (A little variety of users might have enabled SSLv2 manually and can get to take steps to disable it.)
Users of older versions ought to upgrade to a more modern version. we tend to still advocate checking whether or not your non-public secret is exposed elsewhere Other affected software and in-operation systems: Instructions and data for Apache, Postfix, Nginx, Debian, Red Hat Browsers, and other consumers: practical nothing practical that net browsers or different client computer code will do to stop DROWN. only server operators are ready to take action to guard against the attack.
Question 2:
What term describes the amount of risk that remains after the vulnerabilities are classified and the countermeasures have been deployed?
A. Residual risk
B. Impact risk
C. Deferred risk
D. Inherent risk
Correct Answer: A
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Residual_risk
The residual risk is the risk or danger of an action or an event, a method, or a (technical) process that, although being abreast with science, still conceives these dangers, even if all theoretically possible safety measures would be applied (scientifically conceivable measures); in other words, the amount of risk left over after natural or inherent risks have been reduced by risk controls.
Residual risk = (Inherent risk) – (impact of risk controls)
Question 3:
Andrew is an Ethical Hacker who was assigned the task of discovering all the active devices hidden by a restrictive firewall in the IPv4 range in a given target network.
Which of the following host discovery techniques must he use to perform the given task?
A. UDP scan
B. TCP Maimon scan
C. arp ping scan
D. ACK flag probe scan
Correct Answer: C
One of the most common Nmap usage scenarios is scanning an Ethernet LAN. Most LANs, especially those that use the private address range granted by RFC 1918, do not always use the overwhelming majority of IP addresses.
When Nmap attempts to send a raw IP packet, such as an ICMP echo request, the OS must determine a destination hardware (ARP) address, such as the target IP, so that the Ethernet frame can be properly addressed. ..
This is required to issue a series of ARP requests. This is best illustrated by an example where a ping scan is attempted against an Area Ethernet host.
The -send-ip option tells Nmap to send IP-level packets (rather than raw Ethernet), even on area networks.
The Wireshark output of the three ARP requests and their timing has been pasted into the session. Raw IP ping scan example for offline targetsThis example took quite a couple of seconds to finish because the (Linux) OS sent three ARP requests at 1-second intervals before abandoning the host.
Waiting for a few seconds is excessive, as long as the ARP response usually arrives within a few milliseconds. Reducing this timeout period is not a priority for OS vendors, as the overwhelming majority of packets are sent to the host that actually exists.
Nmap, on the other hand, needs to send packets to 16 million IPs given a target like 10.0.0.0/8. Many targets are pinged in parallel, but waiting 2 seconds each is very delayed.
There is another problem with raw IP ping scans on the LAN. If the destination host turns out to be unresponsive, as in the previous example, the source host usually adds an incomplete entry for that destination IP to the kernel ARP table.
ARP tablespaces are finite and some operating systems become unresponsive when full. If Nmap is used in raw mode (-send-ip), Nmap may have to wait a few minutes for the ARP cache entry to expire before continuing host discovery.
ARP scans solve both problems by giving Nmap the highest priority. Nmap issues raw ARP requests and handles retransmissions and timeout periods at its sole discretion. The system ARP cache is bypassed.
The example shows the difference. This ARP scan takes just over a tenth of the time it takes for an equivalent IP.
Example b ARP ping scan of the offline target

In example b, neither the -PR option nor the -send-eth option has any effect.
This is often because ARP has a default scan type on the Area Ethernet network when scanning Ethernet hosts that Nmap discovers.
This includes traditional wired Ethernet as 802.11 wireless networks. As mentioned above, ARP scanning is not only more efficient but also more accurate.
Hosts frequently block IP-based ping packets, but usually cannot block ARP requests or responses and communicate over the network.
Nmap uses ARP instead of all targets on equivalent targets, even if different ping types (such as -PE and -PS) are specified. LAN… If you do not need to attempt an ARP scan at all, specify the end-ip as shown in Example a “Raw IP Ping Scan for Offline Targets”.
If you give Nmap control to send raw Ethernet frames, Nmap can also adjust the source MAC address. If you have the only PowerBook in your security conference room and a large ARP scan is initiated from an Apple-registered MAC address, your head may turn to you.
Use the -spoof-mac option to spoof the MAC address as described in the MAC Address Spoofing section.
Question 4:
Which jailbreaking technique patches the kernel during the device boot so that it becomes jailbroken after each successive reboot?
A. Tethered jailbreaking
B. Semi-tethered jailbreaking
C. Untethered jailbreaking
D. Semi-Untethered jailbreaking
Correct Answer: C
An untethered jailbreak is one that allows a telephone to finish a boot cycle when being pwned with no interruption to jailbreak-oriented practicality.
Untethered jailbreaks are unit the foremost sought-after of all, however, they\’re additionally the foremost difficult to attain due to the powerful exploits and organic process talent they need. associate unbound jailbreak is sent over a physical USB cable association to a laptop or directly on the device itself by the approach of associate application-based exploit, like a website in a campaign.
Upon running associate unbound jailbreak, you\’ll be able to flip your pwned telephone off and on once more while not running the jailbreak tool once more. all of your jailbreak tweaks and apps would then continue in operation with no user intervention necessary.
It\’s been an extended time since IOS has gotten the unbound jailbreak treatment. the foremost recent example was the computer-based Pangu break, which supported most handsets that ran IOS nine.1.
We\’ve additionally witnessed associated unbound jailbreak within the kind of JailbreakMe, that allowed users to pwn their handsets directly from the mobile campaign applications program while not a laptop.
Question 5:
To create a botnet. the attacker can use several techniques to scan vulnerable machines. The attacker first collects Information about a large number of vulnerable machines to create a list. Subsequently, they infect the machines. The list Is divided by assigning half of the list to the newly compromised machines. The scanning process runs simultaneously. This technique ensures the spreading and installation of malicious code in little time.
Which technique is discussed here?
A. Hit-list-scanning technique
B. Topological scanning technique
C. Subnet scanning technique
D. Permutation scanning technique
Correct Answer: A
One of the biggest problems a worm faces in achieving a very fast rate of infection is “getting off the ground.” although a worm spreads exponentially throughout the early stages of infection, the time needed to infect say the first 10,000 hosts dominates the infection time.
There is a straightforward way for an active worm a simple obstacle, that we term hit-list scanning.
Before the worm is free, the worm author collects a listing of say ten,000 to 50,000 potentially vulnerable machines, ideally ones with sensible network connections.
The worm, when released onto an initial machine on this hit list, begins scanning down the list. once it infects a machine, it divides the hit list in half, communicating half to the recipient worm, and keeping the other half.
This fast division ensures that even if only 10-20% of the machines on the hit list are actually vulnerable, an active worm can quickly bear the hit list and establish itself on all vulnerable machines in only some seconds. though the hit list could begin at 200 kilobytes, it quickly shrinks to nothing during the partitioning.
This provides a great benefit in constructing a quick worm by speeding up the initial infection.
The hit list needn’t be perfect: a simple list of machines running a selected server sort could serve, though larger accuracy can improve the unfold.
The hit list itself is generated victimization one or many of the following techniques, ready well before, typically with very little concern of detection. Stealthy scans. Portscans are so common and then widely ignored that even a quick scan of the whole network would be unlikely to attract law enforcement attention or gentle comment within the incident response community.
However, for attackers who wish to be particularly careful, a randomized sneaky scan taking many months would be not possible to attract much attention, as most intrusion detection systems are not currently capable of detecting such low-profile scans.
Some portion of the scan would be out of date by the time it had been used, however abundant of it\’d not. Distributed scanning. an assailant might scan the web using a few dozen to some thousand already-compromised “zombies,” the same as what DDOS attackers assemble in a very fairly routine fashion.
Such distributed scanning has already been seen within the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory received ten throughout the past year.
DNS searches. Assemble a list of domains (for example, by using widely offered spam mail lists, or trolling the address registries).
The DNS will then be searched for the science addresses of mail servers (via mx records) or net servers (by looking for www.domain.com). Spiders.
Net server worms (like Code Red), use Web-crawling techniques the same as search engines so as to produce a list of most Internet-connected websites. this would be unlikely to draw serious attention.
Public surveys. for many potential targets, there may be surveys available listing them, like the Netcraft survey. Just listen.
Some applications, like peer-to-peer networks, wind up advertising many of their servers. Similarly, many previous worms effectively broadcast that the infected machine is vulnerable to further attack. easy, because of its widespread scanning, during the Code Red I infection it was easy to select up the addresses of upwards of 300,000 vulnerable IIS servers because each came knocking on everyone\’s door!
Question 6:
If a token and 4-digit personal identification number (PIN) is used to access a computer system and the token performs offline checking for the correct PIN, what type of attack is possible?
A. Birthday
B. Brute force
C. Man-in-the-middle
D. Smurf
Correct Answer: B
Question 7:
You are attempting to crack LM Manager hashed from Windows 2000 SAM file. You will be using LM Brute force hacking tool for decryption. What encryption algorithm will you be decrypting?
A. MD4
B. DES
C. SHA
D. SSL
Correct Answer: B
Question 8:
Nicolas just found a vulnerability on a public-facing system that is considered a zero-day vulnerability. He sent an email to the owner of the public system describing the problem and how the owner can protect themselves from that vulnerability.
He also sent an email to Microsoft informing them of the problem that their systems are exposed to.
What type of hacker is Nicolas?
A. Red hat
B. white hat
C. Black hat
D. Gray hat
Correct Answer: B
A white hat (or a white hat hacker) is an ethical computer hacker, or a computer security expert, who focuses on penetration testing and other testing methodologies that ensures the safety of an organization\’s information systems.
Ethical hacking may be a term meant to imply a broader category than simply penetration testing. Contrasted with a black hat, a malicious hacker, the name comes from Western films, where heroic and antagonistic cowboys might traditionally wear a white and a black hat respectively.
While a white hat hacker hacks with good intentions with permission, and a black hat hacker, most frequently unauthorized, has malicious intent, there\’s a 3rd kind referred to as a gray hat hacker who hacks with good intentions but sometimes without permission.
White hat hackers can also add teams called “sneakers and/or hacker clubs”, red teams, or tiger teams.
While penetration testing concentrates on attacking software and computer systems from the beginning? scanning ports, examining known defects in protocols and applications running on the system, and patch installations, as an example? ethical hacking may include other things.
A full-blown ethical hack might include emailing staff to invite password details, searching through executives \’s dustbins, and typically breaking and entering, without the knowledge and consent of the targets.
Only the owners, CEOs, and Board Members (stakeholders) who asked for such a censoring of this magnitude are aware. to undertake to duplicate a number of the destructive techniques a true attack might employ, ethical hackers may arrange for cloned test systems, or organize a hack late in the dark while systems are less critical.
In most up-to-date cases these hacks perpetuate for the long-term con (days, if not weeks, of long-term human infiltration into an organization). Some examples include leaving USB/flash key drives with hidden auto-start software in a public area as if someone lost the tiny drive and an unsuspecting employee found it and took it.
Some other methods of completing these include:?
DoS attacks?
Social engineering tactics?
Reverse engineering?
Network security?
Disk and memory forensics?
Vulnerability research?
Security scanners such as:?
W3af?
Nessus?
Burp suite?
Frameworks such as:?
Metasploit?
Training PlatformsThese methods identify and exploit known security vulnerabilities and plan to evade security to realize entry into secured areas.
They\’re ready to do that by hiding software and system `back-doors\’ which will be used as a link to information or access that a non-ethical hacker, also referred to as `black-hat\’ or `grey-hat\’, might want to succeed in.
Question 9:
What is the common name for a vulnerability disclosure program opened by companies In platforms such as HackerOne?
A. Vulnerability hunting program
B. Bug bounty program
C. White-hat hacking program
D. Ethical hacking program
Correct Answer: B
Bug bounty programs allow independent security researchers to report bugs to companies and receive rewards or compensation.
These bugs area unit sometimes security exploits and vulnerabilities, although they will additionally embody method problems, hardware flaws, and so on.
The reports area unit is usually created through a program traveled by an associate degree freelance third party (like Bugcrowd or HackerOne).
The companies can get wind of (and run) a program curated to the organization\’s wants.
Programs are also non-public (invite-only) wherever reports area unit unbroken confidential to the organization or public (where anyone will sign in and join). they will happen over a collection timeframe or without a stopping date (though the second possibility is a lot of common).
Who uses bug bounty programs? Many major organizations use bug bounties as an area of their security program, together with AOL, Android, Apple, Digital Ocean, and Goldman Sachs. you\’ll read an inventory of all the programs offered by major bug bounty suppliers, Bugcrowd and HackerOne, at these links.
Why do corporations use bug bounty programs? Bug bounty programs provide corporations the flexibility to harness an outsized cluster of hackers so as to seek out bugs in their code.
This gives them access to a bigger variety of hackers or testers than they\’d be able to access on a one-on-one basis. It {can also|also will|can even|may also|may} increase the probability that bugs area unit found and reported to them before malicious hackers can exploit them.
It may also be an honest publicity alternative for a firm. As bug bounties became a lot of common, having a bug bounty program will signal to the general public and even regulators that a corporation incorporates a mature security program.
This trend is likely to continue, as some have begun to see bug bounty programs as a business normal that all companies ought to invest in.
Why do researchers and hackers participate in bug bounty programs? Finding and news bugs via a bug bounty program may end up in each money bonus and recognition. In some cases, it will be a good thanks to show real-world expertise once you are looking for employment, or will even facilitate introducing you to parents on the protection team within a company.
This can be full-time income for a few of us, income to supplement employment or a way to point out your skills and find a full-time job.
It may also be fun! it is a nice (legal) probability to check out your skills against huge companies and government agencies.
What area unit the disadvantages of a bug bounty program for independent researchers and hackers? A lot of hackers participate in these varieties of programs, and it will be tough to form a major quantity of cash on the platform.
In order to say the reward, the hacker has to be the primary person to submit the bug to the program. meaning that in applying, you may pay weeks searching for a bug to use, solely to be the person to report it and build no cash.
Roughly ninety-seven of the participants on major bug bounty platforms are haven\’t sold-out a bug. In fact, a 2019 report from HackerOne confirmed that out of quite three hundred,000 registered users, solely around two.5% received a bounty in their time on the platform.
Essentially, most hackers are not creating a lot of cash on these platforms, and really few square measure creating enough to switch to a full-time wage (plus they do not have advantages like vacation days, insurance, and retirement planning).
What square measure the disadvantages of bug bounty programs for organizations? These programs square measure solely helpful if the program ends up in the companies realizing issues that they weren’t able to find themselves (and if they\’ll fix those problems)!
If the company is not mature enough to be able to quickly rectify known problems, a bug bounty program is not the right alternative for his or her company.
Also, any bug bounty program is probably going to draw in an outsized range of submissions, several of which can not be high-quality submissions. a corporation must be ready to cope with the exaggerated volume of alerts, and also the risk of a coffee signal-to-noise magnitude relation (essentially that it\’s probably that they\’re going to receive quite a few unhelpful reports for each useful report).
Additionally, if the program does not attract enough participants (or participants with the incorrect talent set, so participants are not able to establish any bugs), the program is not useful for the companies.
The overwhelming majority of bug bounty participants consider website vulnerabilities (72%, per HackerOn), whereas solely a number (3.5%) value more highly to seek for package vulnerabilities.
This is probably because of the actual fact that hacking in operation systems (like network hardware and memory) needs a big quantity of extremely specialized experience. this implies that firms may even see vital come-on investment for bug bounties on websites, and not for alternative applications, notably those that need specialized experience.
This conjointly implies that organizations which require to look at AN application or website within a selected time frame may not need to rely on a bug bounty as there is no guarantee of once or if they receive reports.
Finally, it is often probably risky to permit freelance researchers to try to penetrate your network. this could end in the public speech act of bugs, inflicting name harm within the limelight (which could end in individuals not eager to purchase the organizations\’ product or service), or speech act of bugs to additional malicious third parties, United Nations agency may use this data to focus on the organization.
Question 10:
A “Server-Side Includes” attack refers to the exploitation of a web application by injecting scripts in HTML pages or executing arbitrary code remotely.
Which web-page file type, if it exists on the web server, is a strong indication that the server is vulnerable to this kind of attack?
A. .stm
B. .html
C. .rss
D. .cms
Correct Answer: A
Question 11:
An attacker runs a Netcat tool to transfer a secret file between two hosts.

He is worried about information being sniffed on the network.
How would the attacker use Netcat to encrypt the information before transmitting it onto the wire?
A. Machine A: netcat -l -p -s password 1234 < testfileMachine B: netcat
B. Machine A: netcat -l -e magic key -p 1234 < testfileMachine B: netcat
C. Machine A: netcat -l -p 1234 < test file -pw passwordMachine B: netcat 1234 -pw password
D. Use crypt cat instead of netcat
Correct Answer: D
Question 12:
Peter extracts the SIDs list from Windows 2000 Server machine using the hacking tool “SIDExtractor”. Here is the output of the SIDs:
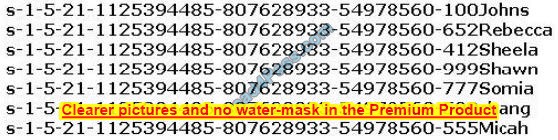
From the above list identify the user account with System Administrator privileges.
A. John
B. Rebecca
C. Sheela
D. Shawn
E. Somia
F. Chang
G. Micah
Correct Answer: F
Question 13:
Which tier in the N-tier application architecture is responsible for moving and processing data between the tiers?
A. Presentation tier
B. Application Layer
C. Logic tier
D. Data tier
Correct Answer: C
Question 14:
Which of the following commands checks for valid users on an SMTP server?
A. RCPT
B. CHK
C. VRFY
D. EXPN
Correct Answer: C
The VRFY commands enable SMTP clients to send an invitation to an SMTP server to verify that mail for a selected user name resides on the server. The VRFY command is defined in RFC 821.
The server sends a response indicating whether the user is local or not, whether mail is going to be forwarded, and so on.
A response of 250 indicates that the user name is local; a response of 251 indicates that the user name isn’t local, but the server can forward the message. The server response includes the mailbox name.
Question 15:
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) has alerted the network administrator to a possibly malicious sequence of packets sent to a Web server in the network\’s external DMZ.
The packet traffic was captured by the IDS and saved to a PCAP file. What type of network tool can be used to determine if these packets are genuinely malicious or simply a false positive?
A. Protocol analyzer
B. Network sniffer
C. Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
D. Vulnerability scanner
Correct Answer: A
…
EC-COUNCIL CEH v12 dumps: It is the best solution for information security professionals to master the basic principles of ethical hacking! Using the latest and effective EC-COUNCIL CEH v12 certification exam program can not only make you progress quickly, but also be sure to help you 100% succeed Pass the exam.
You can take advantage of the free EC-COUNCIL CEH v12 dumps exam questions to help you verify your current learning and improve your professional knowledge! Download 100% Best EC-COUNCIL CEH v12 Certification Exam Solution: EC-COUNCIL CEH v12 dumps with PDF and VCE: https://www.leads4pass.com/312-50v12.html Really helps you pass the exam 100% successfully!

